Stem Cells Ovule Development Embryo
Development
Translational Stem Cell
Research
|
Embryo
development
All multicellular
organisms develop from a single cell, the zygote. We are interested in
understanding how different cell types arranged in the correct body plan
arise from the zygote. For this purpose we have identified genes that instruct cell groups of different destiny and set
up body axes during earliest embryo development. We are using molecular, functional genomic,
and live imaging methods to analyze the mechanisms that specify early
embryo cells and that arrange them into the embryo body.
|
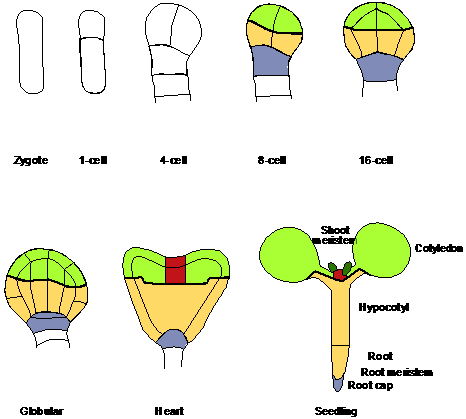
Embryo development of Arabidopsis thaliana:
The development of embryo regions and seedling organs can be followed
from earliest stages on due to a largely invariant cell division pattern (for
a review on plant embryo development see: Laux and
Jürgens, 1997). |
|
Our selected publications on
embryo development:
Ueda, M. and Laux,T. (2012). The origin of the plant body axis. Curr. Op. Plant Biol. 15, 578-584.
Ueda, M., Zhang, Z., and Laux, T. (2011). Transcriptional activation of Arabidopsis axis patterning genes WOX8/9 links zygote polarity to embryo development. Developmental Cell, 20, 264-270.
Zhang, Z. and Laux, T. (2011). The asymmetric division of the Arabidopsis zygote: from cell polarity to an embryo axis. Sex. Plant Reprod. 24, 161-9.
Mallory et al
(2009). Redundant and specific roles
of the ARGONAUTE (AGO) proteins AGO1 and ZLL in development and small
RNA-directed gene silencing. PLoS Genet. 5, e1000646.
Breuninger et al
(2008). Differential expression of WOX genes mediates apical-basal axis
formation in the Arabidopsis embryo. Dev Cell 14, 867-876.
Tucker et al
(2008). Vascular signalling mediated by ZWILLE potentiates WUSCHEL function
during shoot meristem stem cell development in the Arabidopsis embryo.
Development. 17, 2839-2843.
Haecker et
al (2004). Expression dynamics of WOX
genes mark cell fates decisions in early Arabidopsis embryonic patterning.
Development 131, 657-668.
Laux et al (2004)
Genetic regulation of embryonic pattern formation. Plant Cell 16, S190-202. |
|
Stem Cells
Ovule
Development
Embryo
Development
Translational Stem Cell
Research
Last update 18/04/13